malloc
Week 0x9 II
Prof. Calvin
Crypto
Announcements
- Welcome to variously CS 276/CS 540
- Passes of storing structured data
- Antipatterns no more
- Action Items:
- BigRSA due this week.
- list_t possible after this
Data Clump
- C contains a language-mandatory data clump anti-pattern
- This is a data clump - two values that only make sense together.
Today
malloc- Dynamically sized C
free- Unmalloc
Review
Python has no array (NumPy does)
- Historically lists \(\neq\) arrays
- Python lists are closer to being array-lists - an implementation of a list abstract data type using an array data structure
Arrays are:
- Fixed length (replace only, no add/remove)
int arr[10] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 } ;
arr = { 1, 2, 3 } ; // compile error
arr[15] = -1 ; // runtime error - "stack smashing"`- Typed, mostly (still just bits, but of certain size)
Arrays are:
- Just “bits” storing a memory address - no known type or size.
- Arrays exist at fixed location in physical memory.
Review
- We use char * in a function argument to account for arrays of any size.
- What does this mean *physically* within the physical computing device?
- We use “char arr[\(n\)]” in the main function so we know we have enough space.
- What does this mean *physically* within the physical computing device?
Takeaways
| Pointers | Arrays |
|---|---|
Fixed size, like 8 |
Any specified size |
Change with = |
= triggers error |
| Names some bits | Provides/names bits |
| Can describe any array | One specific array |
malloc
Malloc
void *is new, that is how we refer to something but we don’t know to what.- Could be a string, could be a vector of strings (argv) could the message schedule array in SHA.
Malloc
- returns a
void *- This gives the location of some bits
- Those bits can be used however
- The argument
sizeis the number of bytes
- Once we have the
void *, we can use a cast to change it to some other star.- Voilà, something a lot like an array, but of software defined size
- That is, can perform a calculation how much space you need, then dget it.
- “Here is some memory” vs “This memory contains characters”.
- Voilà, something a lot like an array, but of software defined size
Malloc
- Treat this memory region the same way we treat a character array.
- Handwave the null terminator for now.
size_t
- Imagine mallocing all of memory in a single call.
malloc(0xFF...)will either crash or return a void * of zero
- Imagine mallocing all of memory one byte at a time
- This would return 0xFF…
void *, the largest of which would be 0xFF…
- This would return 0xFF…
void *andsize_tare the same size.
void *
#include <stdlib.h> /* for size_t */
#include <assert.h> // for assert
int main() {
assert(sizeof(void *) == sizeof(size_t)) ; /* pass */
assert(sizeof(char) == 1) ; /* pass */
assert(1 == 0) ; /* fail */
return 0;
}- Read more on assert here (or don’t).
From hence
- But where does the memory come from?
- So far, “the stack” - akin to the data structure of the same name
- Operating Systems concept
- For malloc, “the heap” - again akin
- Stack and heap exist in different physical regions of system memory
- So stack memory is near stack memory but distant from heap memory.
Stack & Heap
char arr0[256], arr1[256], arr2[256];
char *ptr0 = malloc(256), *ptr1 = malloc(256), *ptr2 = malloc(256);
printf("%p\n%p\n%p\n%p\n%p\n%p\n", arr0, arr1, arr2, ptr0, ptr1, ptr2) ;- How far are all these things apart from each other:
- Hmmm they all end in zero?
Stack & Heap
- In C, bits are in the stack, where we declare variables, or heap, another special magic place.
- Stack memory in explicit sizes fixed when code is compiled.
- We have only used stack memory so far so we have to fix memory size when we write the code.
Stack & Heap
- In C, bits are in the stack, where we declare variables, or heap, another special magic place.
- A scratchpad space that GCC configures programs to request and the OS allows use of (up to some limit).
- The “magic” is implementation details of the compiler and the operating system.
- The only way we will learn to interface with the heap is malloc.
Stack & Heap
| Stack | Heap |
|---|---|
| Fixed Size | Arbitrary Size |
| Holds Function Variables | Returned by a function (malloc) |
| Defined when compiling by GCC | Defined when running by OS using magic |
Higher/larger (~0xFF...) |
Lower/smaller (~0x00...) |
Credit
| Jenny Chen | Ruohao Guo |
|---|---|
| she/her | she/her |
| Software Engineer | Graduate Research Assistant |
| Apple | Georgia Institute of Technology |
| B.S. Computer Science, 2021, UIUC | B.S. Computer Science, 2021, UIUC |
Stack
Memory layout
- stack: function variables, functions, globals
- heap: malloced variables
- Other stuff for an OS/compilers class
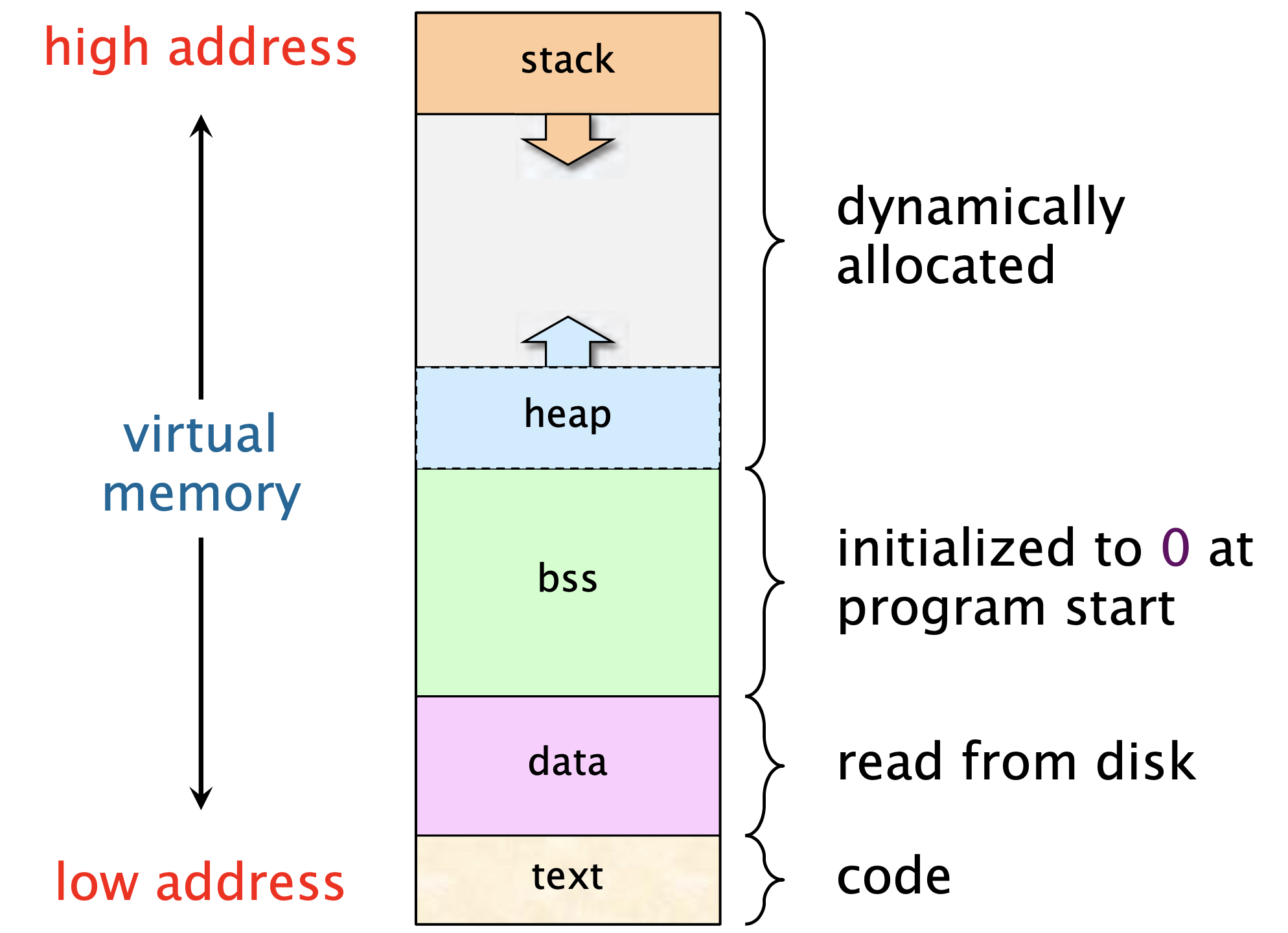
Stack
- Stack reserved when variables declared
- Why C89 requires declares before code
- Why declares require a type with a size.
- Regarded as “growing downwards” from large address to small.

Example
- Allocate
sizeof(int)bytes for variableafor functionmain- A is uninitialized, so the value is undefined.
- Compilers may initialize to a default value
- Assume they don’t.


Example
- Allocate
aformain - Allocate
sizeof(int)bytes for variablebfor functionmain- Store the numerical value
(int)-3in these bytes.
- Store the numerical value


Example
- Allocate
aformain - Allocate
bformain - Allocate
sizeof(int)bytes for variablecformain- Store the numerical value
(int)12345
- Store the numerical value


Function Call
- Allocate
aformain - Allocate
bformain - Allocate
cformain - Allocate
sizeof(int)bytes for variableafor hello- Store
(int)100 - Perhaps
hello.avsmain.a
- Store


Function Call
- Allocate
aformain - Allocate
bformain - Allocate ‘c’ for main’
cformain- Store the numerical value
(int)12345
- Store the numerical value


What of return
- Deallocate the function’s stack.
- “Stack push” the return value.
aalready at the top (bottom) of the stack.- Still
100, no longerhello.a
- Still


What of return
- The calling function does a “stack pop”
- The “stack pop” is stored as
d - The
100never moves.- That’s why we use a stack.


Return
- Push
main.a - Push
main.b=3 - Push
main.c=12345 - Call
hello- Push
hello.a=100 return
- Push
- Pop
a’s value into intomain.d


Stack Discussion?
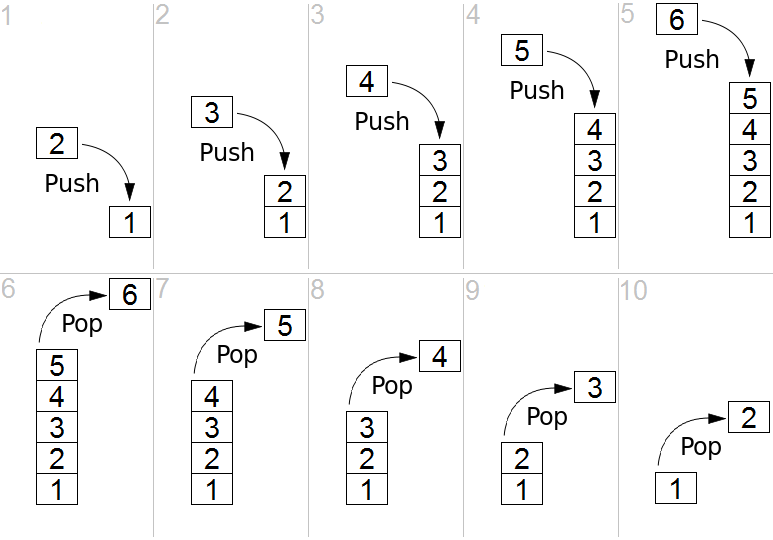

Stack
Heap Example
- Three operations.
- Stack-allocate
sizeof(int *)bytes formain.p. - Heap-allocate
sizeof(int)bytes - Store the address in
p.
- Stack-allocate

- As a reference, we denote this with an arrow rather than by showing a value.
Heap Example
*pis the value of the bits on the heap.- It is an
int - It is 4 bytes
- It is an
pis the value of the bits on the stack.- It is an
int *orvoid * - It is 8 bytes
- It is an


Heap Example
- Malloc
- Store
0atmain.p- Or store
0at the location described bymain.p - Not a push operation!
- Or store


Heap Example
- Stack-allocate
main.q - Heap-allocate
2 * sizeof(int)bytes - Make a note that they are
ints - Store the address in
main.q.


Heap Example
- Malloc
p - Store
0atmain.p - Malloc
q


Heap Example
- Malloc
p - Store
0atmain.p - Malloc
q - Store
1atmain.q


Heap Example
- Malloc
p - Store
0atmain.p - Malloc
q - Store
1atmain.q - Store
2at index1of theintarray which begins atmain.q


Heap Example
- Malloc
p - Store
0atmain.p - Malloc
q - Store
1atmain.q - Store
2inmain.q[1] - Store the value of
main.q(a location) inmain.p


Heap Example
- Malloc
p - Store
0atmain.p - Malloc
q - Store
1atmain.q - Store
2inmain.q[1] - Store the value of
main.q(a location) inmain.p


Today
- ✓
malloc- Dynamically sized C
free- Unmalloc
Free
- p holds address of the heap location holding the integer value
0. - q holds address of the heap location holding the integer array value
1.- Same location as integer array
{1, 2}in this case.
- Same location as integer array

Free
Free
pis a pointer returned frommalloc- We term this type of pointer a “*_Nullable”.
- Not all *’s and *_Nullable’s \[ \{ p \in \text{*_Nullable}\} \subset \{ p \in * \} \]
Free
- Every
mallocin your code should have a correspondingfree - Otherwise you could run out memory (or other problems)
Memory Leak
- p holds a *_Nullable.
- q holds a *_Nullable.

Memory Leak
- p, q holds a *_Nullable.
- “old
p” forgotten!

Your poor OS
- Your poor OS is on contract to protect that
1you left in “oldp” forever! - This is why sometimes restarting your computer causes it work.
- E.g. Java, Python have a “garbage collector” that frees memory for you and causes you code to run 500 times (not always an exaggeration) slower.
- Also if you try really hard you can memory leak Python.
Instead
free(p)and the bytes return to circulation.0persists until overwritten*

Valgrind
- Verifying that all memory has been freed isn’t easy!
- I recommend use of
valgrind - I won’t teach Valgrind this term but may show it time to time.
leaky.c
- Write a quick memory leaking program:
Valgrind
- Compile a run within
valgrind
$ gcc leaky.c
$ valgrind ./a.out
==1331== Memcheck, a memory error detector
==1331== Copyright (C) 2002-2017, and GNU GPL'd, by Julian Seward et al.
==1331== Using Valgrind-3.18.1 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==1331== Command: ./a.out
==1331==
==1331==
==1331== HEAP SUMMARY:
==1331== in use at exit: 8 bytes in 2 blocks
==1331== total heap usage: 2 allocs, 0 frees, 8 bytes allocated
==1331==
==1331== LEAK SUMMARY:
==1331== definitely lost: 4 bytes in 1 blocks
==1331== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==1331== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==1331== still reachable: 4 bytes in 1 blocks
==1331== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==1331== Rerun with --leak-check=full to see details of leaked memory
==1331==
==1331== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s
==1331== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)Emph
- Those are these 4 bytes:
Fix it
leaky.c
“Good Enough”
- It is possible to confuse Valgrind (and I intend to do so if we have time)
- As a rule, if it confused Valgrind it likely contains some antipattern.
- Up to debate with my planned example.
Free + Leak = Freak
We can generate a silly outcome at high probability by:
- Store value to heap
- Memory leak
- Check value
Freak
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main() {
int *p = malloc(sizeof(int)), *q, i ;
*p = 1 ;
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
free(p) ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < 1000000 ; i++) {
q = malloc(0xFF) ;
}
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
}- Run it:
Without free
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main() {
int *p = malloc(sizeof(int)), *q, i ;
*p = 1 ;
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < 1000000 ; i++) {
q = malloc(0xFF) ;
}
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
}- Run it:
Without leaks
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main() {
int *p = malloc(sizeof(int)), *q, i ;
*p = 1 ;
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
free(p)
printf("%d\n", *p) ;
}- Run it:
1is unprotected but not yet overwritten.
Today
- ✓
malloc- Dynamically sized C
- ✓
free- Unmalloc
- Memory-adjacent techniques?
- If time
Overthinking
- It’s just bits.
- A void *, a size_t, and a character array of length 8 walk into a compiler.
- The compiler asks “Why the long int”?
- In running code, there is no distinction between any of these: each is simply 64 bits.
- The compiler maintains the distinction when generating code to make writing code easier for humans.
| Type | Use | Print code | sizeof(), usually |
|---|---|---|---|
void * |
a memory location | %p |
8 |
size_t |
size of some memory | %zu or %ld |
8 |
char buf[8] |
8 values of size 1 | %s |
8 |
long,long int,int64_t |
\(\text{abs}(x) <= 2^{63}\) | %ld |
8 |
Casting
- Casting avoids
gccwarnings/errors:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void main() {
char *buf[8];
void *p = (void *)buf;
void *q = malloc(1);
size_t dist = (size_t)p - (size_t)q;
printf("q was malloc'ed %zu bytes from stack allocated p.\n", dist);
}- See it:
Implicit Cast
- Can infer casts, but some draw warnings:
$ cat leaky.c
void main() {
char buf[2] = "h";
void *letter = buf;
void *ptr = 'h';
}
$ gcc leaky.c
leaky.c: In function ‘main’:
leaky.c:7:25: warning: initialization of ‘void *’ from ‘int’ makes pointer from integer without a cast [-Wint-conversio]
7 | void *ptr = 'h';
|
$ python3 -c 'print(ord("h"))'
104 - char array to
void *is fine - both addresses
Documentation
- Sometimes we can use casts to make it more clear what our code should be doing.
- I like void casts, they remind me of Python “_ =” which I use in notebooks to discard output.
Takeaways
- Cast the return value of malloc.
int main() {
char *ptr = malloc(8) ; // error-prone, ambigious
char *str = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 8) ; // more intentional
}- Much bigger deal when using types of size other than one, or of unknown size.
Pointer Arithmetic
- Wait a minute…
sizeof(int) != 1. - So
qis must be some value other than1away fromq[1] - Yet we do not address the next int in an array by saying
q[1*sizeof(int)]

Overload
- People are allowed to like things, so you are allowed to like this.
- I don’t.
>>> x, y, s, t = 1, 2, "h", "i"
>>> x + y 3
>>> x + s
Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'
>>> s + t 'hi'
>>>- This is called operator overloading.
- It’s not allowed in C.
Two many gcc’s
- If you add strings together,
gccstops you.
- Thanks,
gcc.
leaky.c: In function ‘main’:
leaky.c:2:13: error: invalid operands to binary + (have ‘char *’ and ‘char *’)
2 | "a" + "b";
| ~~~ ^
| | |
| | char *
| char *- What does “binary” mean ? (Hint: MATH 251W)
Trust gcc
- Let’s do a cast and an addition
Trust!
- At least it’s consistent.
printf("%p + %p = %p \n", (void *)p, (void *)x, (void *)((char *)p + x)) ;
printf("%p + %p = %p \n", (void *)p, (void *)x, (void *)((int *)p + x)) ;
printf("%p + %p = %p \n", (void *)p, (void *)x, (void *)((long *)p + x)) ;`- All 0x108 I’m sure.
- Get it?
Overload?
- “operator overloading… not allowed in C.”
- Addition and subtraction… are(?) overloaded
- Realistically, not quite (not commutative)
- Add a (1) location and (2) integer
- int * + int
- int * + long
- char * + int
- long * + char
On []
- Pointer arithmetic too.
int arr[4] = { 0x10, 0x100, 0x1000, 0x10000 } ;
printf(" arr+1 : %p\n", arr+1) ;
printf("*(arr+1): %p\n", *(arr+1)) ;
printf("(*arr+1): %p\n", (*arr+1)) ;
printf(" arr[1]: %p\n", arr[1]) ;- See it.
Unary &
- & is both a unary and binary operator in C, like - (minus)
&
- Unary
&is inverse*
int main() {
int x = 0xF0, y = 0x0F, *p; // just unique vals
p = &y;
printf("*p = %x, p = %p\n", *p, p);
printf(" y = %x, &y = %p\n", y, &y);
}p = &y\(\implies\)*p = y
&
*is not (quite) inverse&
int main() {
int x = 0xF0, y = 0x0F, *p; // just unique vals
*p = y;
printf("*p = %x, p = %p\n", *p, p);
printf(" y = %x, &y = %p\n", y, &y);
}*p = y\(\not\!\!\!\implies\)p = &y
Malloc fail
There is no guarantee
mallocworked- Imagine
malloc(∞) - Rather, it is very likely to return correctly if used mindfully.
- But you must check.
- Imagine
Force fail
Today
- ✓
malloc- Dynamically sized C
- ✓
free- Unmalloc
- ✓ Memory-adjacent techniques?
- If time